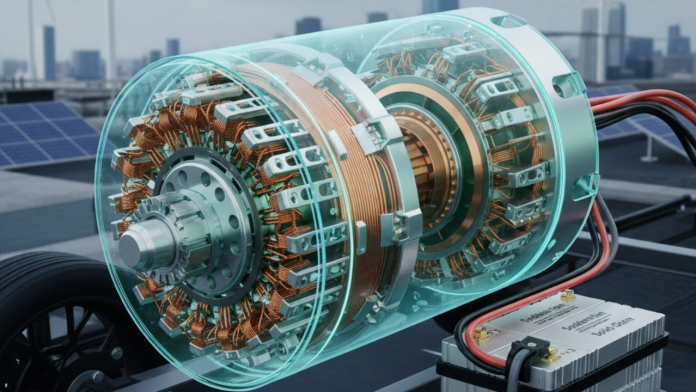
The uncertainty in the supply of rare-earth minerals has accelerated the adoption of rare-earths free EV technologies with multiple alternatives. This switch is both cost-effective and sustainable.
Some of the techniques under practice include: –
Synchronous Reluctance Motors (SynRM)
Unlike traditional motors, these operate without an induced current in the rotor, relying on ‘Magnetic Synchronization’ for movement. They harness the natural properties of magnetic reluctance to deliver unparalleled performance.
The rotor in the SynRM is crafted with multiple layers of laminated steel, which forms a path for the magnetic flux, eliminating the need for conductors or permanent magnets.
Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM)
This generates torque through magnetic attraction and repulsion between the stator and the rotor, through the stator’s changing magnetic field. This mechanism is possible even with a simple construction and the use of readily available materials.
Such a motor is resilient to harsh conditions, mechanical stress, and electrical faults.
Induction Motors
Induction motors, are known for their robustness, low-cost, and simplicity. Using copper/aluminum windings on the rotor, they create a magnetic field through electromagnetic induction from the stator, eliminating the need for magnets entirely.
Externally Excited Synchronous Motors (EESM)
These motors generate their rotor’s magnetic field from an external DC source, allowing for control of metrics like power factor and speed. Their adjustable magnetic field increases the motor’s efficiency across a wider range of speeds and loads.
Ferrite-based magnets
These ceramic magnets, made from iron oxide are used as alternatives to permanent magnets. Despite their reduced power, their magnetic fields are strengthened and the torque is assisted by the rotor’s changing magnetic reluctance.
Innovations with such rare-earth free technology options can help boost the Indian EV manufacturing ability. Ultimately, it will also address the geopolitical instability in the supply-chains of rare earth minerals, which were once considered the core of EVs.